Strategic Plan
BART's Strategic Plan Framework (PDF) was adopted by the Board of Directors in 2015. The Framework includes a mission, vision, goals, and strategies.
Station Access Policy
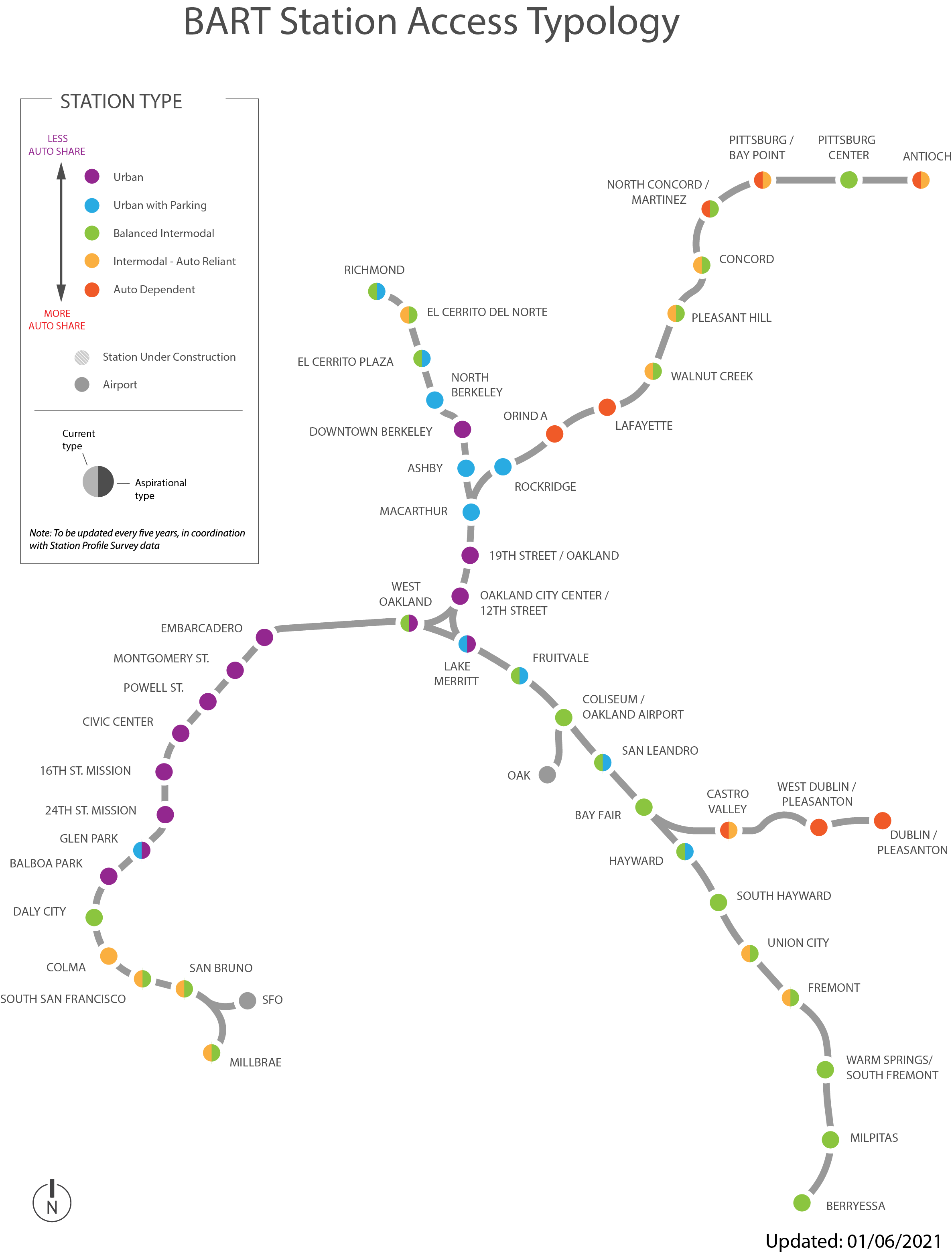
In June 2016, the BART Board adopted a new Station Access Policy to guide access practices and investments through 2025. Access investment priorities at each station are guided by the station's assigned access type, shown above. To inform development of a new policy, BART prepared a background report that identifies the current policy context, discusses recent trends, and examines selected best practices from other transit agencies. Read more about our efforts to update the policy and view all of BART's previous access policies and practices at www.bart.gov/AccessPolicy.
Expansion Policy
BART’s System Expansion Policy states goals and strategies for expanding the system including criteria for evaluating expansion opportunities. To meet the needs of an evolving Bay Area, BART is revisiting our System Expansion Policy.
The Planning Department at BART assesses strategic opportunities for system expansion by conducting corridor studies for future BART services, assessing alternative methods for expanding transit services in the region, completing assessments of environmental impacts of proposed projects, and analyzing opportunities for new stations within the existing system (infill stations). Learn more at https://www.bart.gov/about/planning/strategic.
Multimodal Access Design Guidelines
Following the Board's adoption of the Station Access Policy in 2016, design guidelines were developed to improve pedestrian, bicycle, and transit access at BART stations.
BART’s Multimodal Access Design Guidelines provide easy-to-use guidance and minimum/maximum and recommended standards for planning access within BART’s station areas. This guide covers the area from the station faregates to the edge of BART’s property, and applies to connecting intersections.
Transit-Oriented Development (TOD) And Affordable Housing Policies
BART’s Transit-Oriented Development (TOD) program aims to help create great communities near stations through development of BART property and partnerships with cities. Read related policies, guidelines, procedures, work plans, studies and details about AB 2923 implementation at www.bart.gov/TOD
The TOD Policy also incorporates the Affordable Housing Policy, adopted by the BART Board in January 2016.
Sustainability
BART's Sustainability Policy (pdf) - BART is committed to advancing regional sustainability by providing safe, affordable, equitable, and environmentally-friendly transit to move people to jobs, recreation and services. BART incorporates cost-effective sustainability through fulfillment of the following goals:
- Advance smart land use, livable neighborhoods and sustainable access to transit.
- Choose sustainable materials, construction methods, and operations practices.
- Use energy, water, and other resources efficiently.
- Reduce harmful emissions and waste generation.
- Respond to risks from extreme weather, earthquakes, and other potential disruptions.
- Improve patron and employee health and experience.
- Serve as a leader in sustainability for transit agencies and the communities that BART serves.
Learn more in our sustainability section.
Art in Transit Policy
In 2015, the BART Board adopted its first Art in Transit Policy, which was updated by the Board in June 2018 to include a funding strategy for the Art Program. More information on BART's art program can be found at www.bart.gov/art.